
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Julong College, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
2 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
Cnoidal waves are a type of nonlinear periodic wave solutions of the nonlinear dynamic equations. They are well known in fluid dynamics, but it is not the case in optics. In this paper we show both experimentally and numerically that cnoidal waves could be formed in a fiber laser either in the net normal or net anomalous cavity dispersion regime, especially because, as the pump power is increased, the formed cnoidal waves could eventually evolve into a train of bright (in the net anomalous cavity dispersion regime) or dark (in the net normal cavity dispersion regime) solitons. Numerical simulations of the laser operation based on the extended nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLSE) have well reproduced the experimental observations. The result not only explains why solitons can still be formed in a fiber laser even without mode locking but also suggests a new effective way of automatic stable periodic pulse train generation in lasers with a nonlinear cavity.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(3): 543
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 DSO National Laboratories, 118225 Singapore, Singapore
2 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 639798 Singapore, Singapore
3 e-mail: seon.yoo@ntu.edu.sg
4 e-mail: csonglia@dso.org.sg
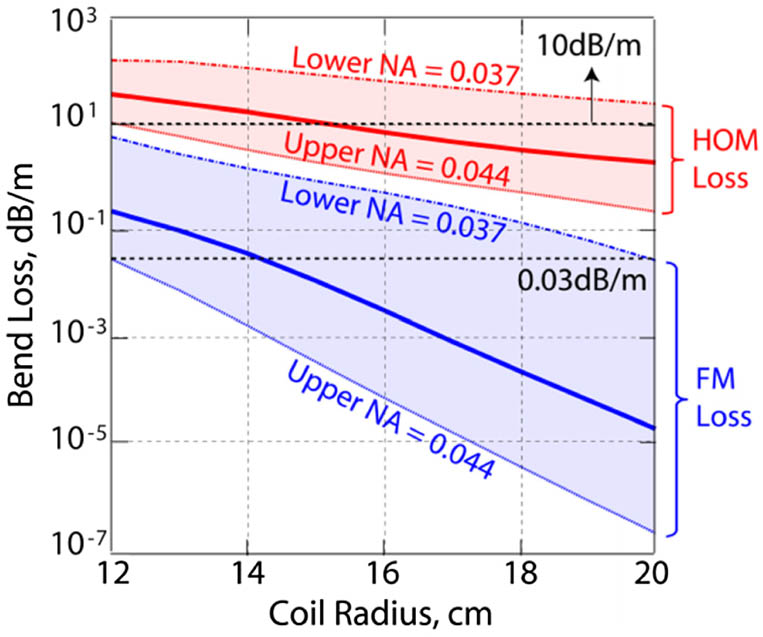
A short absorption length ytterbium (Yb)-doped large-mode area (LMA) fiber is presented as a step forward to mitigate the stern problem of nonlinear scatterings in a tandem pumping scheme adopted for high-power fiber laser. The short absorption length was realized by incorporating high Yb concentration in the fiber core. Furthermore, by replacing the inherent silica cladding with a Ge-doped cladding, we were able to obtain low core numerical aperture (NA) and negate the detrimental effect of index-raising by high Yb concentrations. This overcomes the long-standing limitation in step-index Yb-doped fibers (YDFs) where high cladding absorption inevitably results in high NA, thus hampering single-mode operation. We report an LMA () YDF with NA of 0.04 and absorption of 27 dB/m at 976 nm—both traits promote power scaling of single-mode tandem pumped fiber lasers. To our knowledge, this is the highest cladding absorption attained in a low-NA step-index fiber to date. An all-fiber tandem-pumped amplifier was built using only of the YDF. The amplifier delivered a near-Gaussian beam () at 836 W output power (pump power limited) with a high slope efficiency of . Thanks to the short length and the tandem pumping, no indication of limiting factors such as stimulated Raman scattering, photodarkening, and transverse mode instability was observed.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(10): 10001599
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Laser Engineering
,
Beijing University of Technology
,
Beijing 100124
,
China
2 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
,
Nanyang Technological University
,
Singapore
In 2018, the journal High Power Laser Science and Engineering produced a Special Issue on Fibres for High Power Lasers. Nowadays, fibre-based laser sources have found extensive applications both in industry and in scientific research. The scope of the special issue was to span the latest developments on the fast developing fibre-based high-power lasers and amplifiers. The topics invited for inclusion were:
fibre laser gain fibres high-power fibre amplifier High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(4): 04000e54
Department of Information and Communications, Kwangju Institute of Science and Technology 1 Oryong-dong, Buk-gu. Gwangju, 500-712, Korea





